This website doesn't use cookies, but it does embed YouTube videos. These videos may use cookies to collect data and provide personalized ads. By clicking "Accept", you consent to YouTube's use of cookies on your device. For more information, please visit Google's Cookie Policy.
Wheels communicates climate change science using kinetic structures and a web app, which provides information about the selected datasets and their significance for climate change.

Please accept cookies to watch this video
The transition into the era of the Anthropocene was an exploitative process accompanied by turning wheels, mastering time and productivity. Wheels are used to measure work time, to carve trenches into the earth and harvest its resources, to transform materials into refined products, and to transport goods around the planet. The industrial revolution was accompanied by turning wheels and since then human activities have changed the world's climate by releasing greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere. A comfortable western lifestyle comes with an enormous cost on people, animals and the planet and, while the turning wheel of a clock can always be turned back to its beginning, the changes to our world due to our progress and growth are permanent. Carbon dioxide can stay in the atmosphere for more than a thousand years once released by burning fossil fuels, solid waste or trees. While there are many movements in the right direction, overall the current global policies are not drastic enough considering the 66% chance of a global increase in temperature of 2.8°C by 2050. Scientists have collected data about the earth's past climate via ice cores, tree rings, glacier lengths, pollen remains and ocean sediments as well as studying changes in the earth's orbit around the sun. With today's data from satellites and other sensors they can measure the reflectivity of the earth, temperatures, sea levels, ice and snow coverage and atmospheric gas composition.
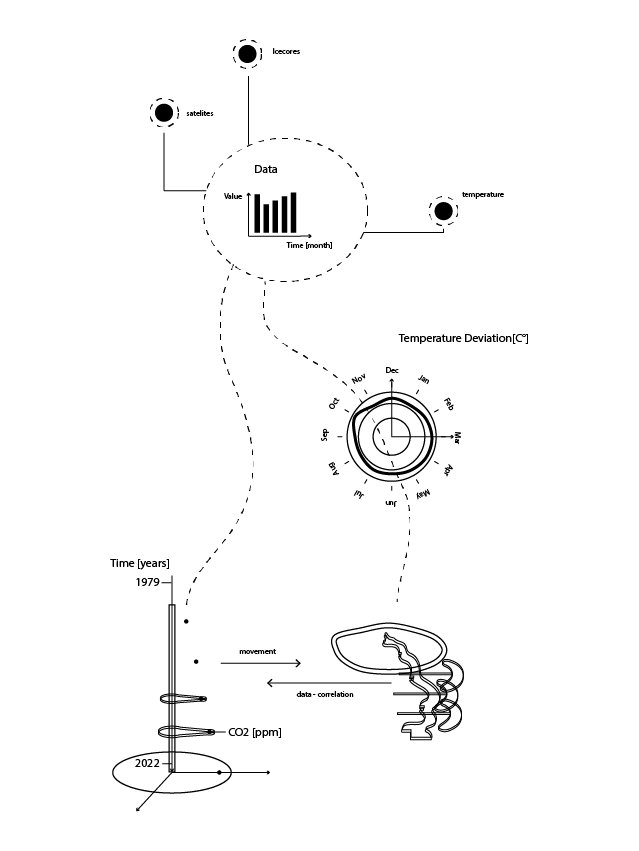
With this collected data scientist model the past, predict the future and measure change. Climate change is caused by a web of actors and dependencies, policies and industries, individual behaviours and systemic stagnation and it calls for interdisciplinary approaches to illuminate our current situation, to highlight the paths ahead, to find the (local) knots and to untangle our fate together. Art is a useful tool for communicating climate change as it has the ability to show the urgency of numbers and draw intuitive images of complex systems and enhance scientific facts with the metaphysical, activism, politics and emotion. Ed Hawkins climate spiral shows the power of finding the right form to visualise scientific data. By plotting the monthly global average temperature anomaly in a circular line plot he draws a dire image of the drastic temperature increase since 1850. This graphic was so successful that it was viewed over 3.4 million times in its first year on twitter.
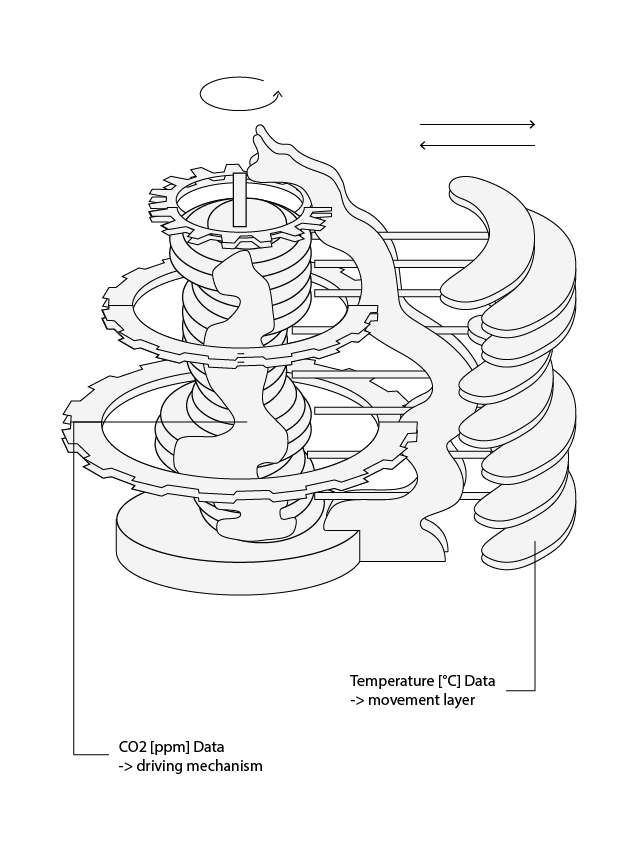

Wheels communicates climate change science in the form of kinetic structures. These machines are three-dimensional data structures of correlated selected climate change data which rotate around the axis of the object. Due to the objects inner mechanism the rotation creates a movement between the correlated data sets pushing and pulling between the drivers and impacts of climate change. The three dimensional mapping of the data as well as the kinetic animation should show the data in a more urgent context while subtly referring to the mechanism of a clock, the industrialisation and the stagnant political process on climate change.
Explore
Datastructures
C02 vs Temperature